IMMUNE SYSTEM - LIFESTYLE TIPS, VITAMINS, AND 16 FOODS TO BOOST YOUR IMMUNE SYSTEM NATURALLY
Your immune system is your body’s version of the military and defence. It keeps you safe against diseases, infections, and helps you heal after injury. Therefore, if your immune system is in good shape – you will have a strong army. However, sometimes your immune system fails, a virus or a germ takes over and makes you sick.
Also our age affects our immune response and as we grow older, our immune system goes weaker, which in turn leads to more infections. Therefore, compared with younger people, the elderly are more likely to catch infectious diseases and more likely to die from them.
So, is it possible to interfere in this process and make your immune system strong?
The good news is - yes, it is possible to boost your immune system. However, it's a huge project as the immune system is precisely that — a system, not a single entity.
To work at its best, your immune system needs harmony and balance. So, to boost your immune system you will have to take care of your whole body and soul. Here are 13 ways to do that.
13 Healthy Ways to Strengthen Your Immune System
The first and most important step is to choose a healthy lifestyle and follow general good-health guidelines. Every cell in your body, including your immune system, works at its best when you protect it from environmental threats and support by healthy-living tactics such as these listed shortly in the following table.
[table id=4 /]
1. Don`t Smoke
Smoking is bad for your health, so it's also bad for your immune system. Here's the list of health hazards associated with light and intermittent smoking:
- heart disease due to high blood pressure and cholesterol-clogged arteries
- weakened aorta (an aortic aneurysm)
- premature death from cardiovascular disease
- lung, esophageal, stomach, and pancreatic cancer
- respiratory tract infections
- delayed conception in women and poorer sperm function in men
- slower recovery from torn cartilage and other injuries
- cataract
- increased frailty in older men and women
- poorer health-related quality of life.
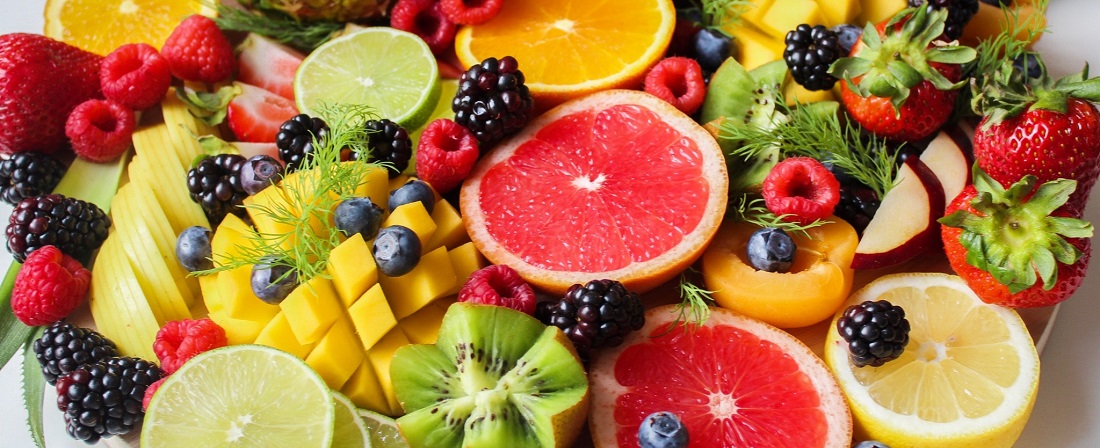
2. Diet High In Fruits And Vegetables - 16 Strong Immune System Boosters
Feeding your body certain foods may help keep your immune system strong. Plan your diet and include at least 3 out of these 16 strong immune system boosters.
1. Citrus fruits
It is thought that Vitamin C boosts the production of white blood cells. Because your body doesn't produce or store it, you need daily vitamin C for continued health. Almost all citrus fruits contain high amounts of vitamin C. These are key to fighting infections. Popular citrus fruits include:
- Grapefruit
- Oranges
- Tangerines
- Lemons
- Limes
- Clementines
2. Red bell peppers
Citrus fruits are excellent sources of vitamin C, but not the only ones. Red bell peppers hold double the amount of vitamin C compared to citrus fruits and are also a great source of beta carotene. In addition to strengthening your immune system, vitamin C may also contribute to maintaining healthy skin. Beta carotene helps keep your eyes and skin healthy.
3. Ginger
Ginger has antibacterial properties, therefore it may help improve your immune system. While it's used in many sweet desserts, ginger packs some heat in the form of gingerol, a relative of capsaicin. Ginger may also help decrease chronic pain, prevent nausea, soothe an upset stomach and may possess cholesterol-lowering properties, according to recent animal research.

4. Broccoli
According to one study, one ingredient found in broccoli and other similar vegetables may help enhance your immune system. Broccoli is one of the most beneficial vegetables because it's packed with fiber, antioxidants, minerals and vitamins such as vitamins A, C, and E. To keep its power - cook it as little as possible, or even better, eat it raw.
5. Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, which is known to have anti-inflammatory properties that help boost immunity.
6. Garlic
Garlic`s health improving properties come from a heavy concentration of sulfur-containing compounds, such as allicin that help the immune system fight germ. It adds a little zing to food and it's a must-have for your health. According to the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, garlic may also contribute to lowering blood pressure.
7. Onion
Onions contain high levels of vitamin C, other nutrients and phytochemicals, many of which provide possible benefits for your immune system. Onions also contain a group of complex carbohydrates fructans that provide soluble fiber and pass through the small intestine without being digested and go on to the large intestine. In the large intestine they supply food for the good bacteria in your colon, such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli. As fructans encourage growth of probiotics, they are referred to as prebiotics.

8. Spinach
Greens such as kale, spinach, and Swiss chard are immune-boosting foods that contain high levels of vitamin C, which not only packs a powerful antioxidant punch, but helps also fight off infection and restore other antioxidants in the body such as vitamin E.
Green leafy vegetables also contain folate and beta carotene, which may increase the infection-fighting capability of your immune system. Similar to broccoli, spinach is healthiest when it’s cooked as little as possible so that it retains its nutrients.
However, light cooking boosts its vitamin A.
9. Green tea
Polyphenols, potent plant antioxidants, are what's believed to give green tea its immune-boosting effects. One study proposed that a specific type of polyphenols called catechins may eliminate influenza viruses.
Also, both green and black tea contain flavonoids, a type of antioxidants which protect your cells against free radicals. Green tea really shines in its levels of epigallocatechin gallate, or EGCG, another powerful antioxidant which has been shown to enhance immune function. Green tea is steamed and not fermented, so the EGCG is preserved.
Black tea on the other hand goes through a fermentation process that destroys a huge amount of the EGCG. Green tea is also a great source of the amino acid L-theanine which may help in the production of germ-fighting compounds in your T-cells.
10. Yogurt
While more research needs to be done, there's some evidence that some strains of probiotics can help boost the immune system to fight diseases and promote a healthy digestive tract. Look for yogurts that have "live and active cultures" printed on the label, like for example Greek yogurt.
Some fortified yogurts may also be a good source of vitamin D. Vitamin D is thought to boost our body’s natural defenses against diseases.
11. Almonds
According to a research, even after the almonds had been digested in the gut, there was still an increase in the immune system's defence against viruses.
Next to vitamin C, vitamin E is the second crucial vitamin for a healthy immune system and preventing and fighting off colds. However, it’s a fat-soluble vitamin, so it requires the presence of fat to absorb properly.
Almonds are filled with the vitamin E and also contain healthy fats. A half-cup portion provides nearly 100% of the suggested daily quantity of vitamin E.

12. Kiwi
Kiwis are full of vitamin C. For example, just 1 cup of kiwis gives you about 273% of your daily suggested value. Vitamin C is a vital nutrient when it comes to warding off diseases and improving your immune system. Like papayas, kiwis are packed with a huge amount of other essential nutrients, such as vitamin K, folate and potassium.
Vitamin C in kiwi promotes white blood cells to fight infection, and other nutrients in kiwi help the rest of your body to work properly.
13. Papaya
Papaya is another fruit loaded with vitamin C. One single papaya contains 224% of the daily recommended amount of vitamin C. Papayas also contain a digestive enzyme called papain which have anti-inflammatory properties.
Papayas have decent amounts of potassium, B vitamins, and folate, all of which are beneficial to your overall health.
14. Sunflower seeds
These seeds contain selenium and are also a good source of vitamin E. Just a quarter-cup serving contains 82% of the daily recommended amount. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant, helps to fight free radicals, maintain immune system function and assists in maintaining healthy skin, hair and nails.
Sunflower seeds are also packed with other nutrients such as phosphorous, magnesium, and vitamin B-6.
15. Poultry
Chicken and turkey contain vitamin B-6. Around 3 ounces of light chicken or turkey meat holds 40 to 50% of your daily suggested amount of B-6. Vitamin B-6 is a vital component in many chemical reactions that take place in the body including in formation of new and healthy red blood cells. Therefore, take time for cooking broth by boiling chicken bones.
The end result contains gelatin, chondroitin, and other nutrients that are helpful for your gut and immune system.
16. Shellfish
Some types of shellfish contain zinc. Zinc affects multiple aspects of the immune system and is critical for normal development and function of cells that mediate innate immunity. Therefore, our bodies need zinc so that our immune cells can function as intended. Varieties of shellfish that are high in zinc include:
- Crab
- Clams
- Lobster
- Mussels
Keep in mind that you don’t want to have more than the daily recommended amount of zinc in your diet, because zinc overdose may actually impede immune system function. For adult men, it’s 11 milligrams (mg), and for women, it’s 8 mg.
3. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise is one of the key factors in being healthy and having strong immune system. It betters cardiovascular health, promotes good circulation (which allows the cells and substances of the immune system to move through the body freely and do their job effectively), lowers blood pressure, helps manage body weight, helps to boost the immune system and defends against a variety of diseases.
So, the same way as a healthy diet, exercise can also promote general good health and therefore a stronger immune system.
4. Maintain A Healthy Weight
In fact, obesity is characterized by researchers as “ a state of low-grade, chronic inflammation.” This means that increased fat cells put your body in a constant state of stress and immune response.
However, if your body is always in a condition of inflammation, your immune system is constantly “turned on.” Therefore, try to maintain healthy weight, and your immune system will be thankful.
5. Get A Good Night’s Sleep
Your body can’t function correctly if you aren’t sleeping well. Its necessary to get more than five hours of sleep a night, otherwise you and your immune system may become depressed. This leaves you open to colds, flu, and infection.
If you run around like insane, and then find yourself unwell? That’s because your immune system getting its revenge.
6. If You Have To Drink Alcohol, Drink Only In Moderation
Alcohol damages mucosal immunity in the gut and lower respiratory system. You don't even have to be a chronic alcohol drinker to have a negative effect on your health.
Even one study shows that acute binge drinking also has an impact on the immune system.
7. Try To Minimize Stress
Your immune system is ready for anything you can throw at it. But it can only handle so much.
Stress has a serious impact on your immune system. During stress, a series of events release cortisol, adrenaline, and other stress hormones from the adrenal gland. Together they help your body cope with stress. Normally, cortisol is helpful because it decreases the inflammation in the body that results from the immune responses caused by stress.
Several health problems such as stomach upset, nettle rash, and even heart disease, are linked to the effects of emotional stress. So if a person is chronically stressed, stress hormones can affect the way the body functions over time. This increases your risk of health problems, including:
- anxiety
- depression
- digestive issues
- heart disease
- sleep disorders
- weight gain
- problems with memory and concentration
It’s important to find healthy ways to deal with your stress. Some good ways to reduce stress include:
- meditation
- yoga
- acupuncture
- talk therapy
- art therapy
- exercise
- eating healthfully
8. Moderate Sun Exposure
Exposure to sunlight is how your body naturally produces vitamin D. It’s even said to be good for people with autoimmune disorders.
However, if you are light-skinned, you need only around 10 minutes on a sunny day to get all the vitamin D you need. Too much sun can lead to non-permanent harm to your immune system and finally cause skin cancer. So, some sun is good for you, but you need to protect your skin when you plan to spend time outside.
When the sun is very strong, you should also wear protective clothing, such as:
- Long-sleeved shirts
- Long pants
- Wide-brimmed hats
- Sunglasses
Also, stay mostly in the shade when the sun’s rays are strongest, between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m.
9. Germs Keep You Healthy
Your gut is filled with tons of good bacteria and other things to help you digest your food.
These good bacteria in your gastrointestinal tract provide vital health benefits to you and regulate immune homeostasis. While imbalance in your microbiota can cause dysbiosis, immune dysregulation, leading to autoimmune disorders.
Results of evidence-based analysis from human studies and animal models suggest that probiotics have potential for clinical effectiveness on intestinal diseases, including infectious diarrhea, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, atopic diseases, necrotizing enterocolitis, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and extraintestinal diseases, such as allergy. The most commonly used probiotic microorganisms against these pathogens are:
- Lactobacillus acidophilus,
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG,
- Saccharomyces boulardii,
- Bifidobacterium bifidum,
- Bacillus coagulans.
10. Practice good hygiene. Washing your hands regularly can prevent infections
Soap and water can remove bacteria from your hands and keep it from reaching your eyes, nose and mouth - and from infecting you. A University of Colorado study showed that students who washed their hands more often experienced fewer incidences of the common cold and flu.

11. Laugh
Laughter helps your immune system. The saying goes that laughter is the best medicine, and there’s truth to that. Because of laughing your body releases dopamine and other feel-good chemicals in the brain that may help reduce stress.
Laughing 20 minutes daily may not keep the doctor away, however it may help keep your immune system function better.
12. Take Vitamins
If you suspect your diet is not providing you with all your micronutrient needs — maybe, for instance, you don't like vegetables — taking a daily multivitamin and mineral supplement may also have other health benefits in addition to the impact on your immune system. Taking a huge amount of a single vitamin does not. More is not necessarily better.
There is some evidence that various micronutrient deficiencies — for example, deficiencies of zinc, selenium, iron, copper, folic acid, and vitamins A, D, B6, C, and E — alter immune responses in animals, as measured in the test tube.
13. Coldwater Swimming
The effects of cold water on the immune system have been studied widely and there’s a reason why so many people who participate in cold water swimming are rarely sick.
Most health experts agree that the reason winter is "cold and flu season" is not that people are cold, but that they spend more time indoors, in closer contact with other people who can pass on their germs.
NB! The information provided here is for informational purposes only, so do not consider it as health care or medical diagnosis and treatment. Do not consider this information as a guarantee of the results you want to achieve. In addition, this information is not intended to replace the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional.
Even more, you should not use it to diagnose or treat a health problem. Before changing or discontinuing your existing medication, treatment, or care, or taking any dietary supplements, be sure to consult with your healthcare professional or doctor before starting any diet or program, or if you suspect you may have a medical condition.
Written by Maria-Helena Loik
This article was first published on Ecosh.com
Sources: Health.harvard.edu, Healthline.com, Lifehack.org, Healthyeating.sfgate.com, Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Photo credit: Pexels.com, Pixabay.com